What Do You Need To Know Before You Entry PCB Industry
Mar 31, 2025
FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) is a common substrate used to manufacture printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is a glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin composite material with good mechanical strength, heat resistance, electrical insulation and flame retardancy.
Main features of FR4
Material composition:
Glass fiber cloth (provides mechanical strength)
Epoxy resin (provides insulation and heat resistance)
Flame retardant (makes it reach UL94-V0 flame retardant grade)
Performance characteristics:
High temperature resistance (usually can withstand 130-150°C, some high TG FR4 can reach 170-180°C)
High mechanical strength (bending resistance, impact resistance)
Good electrical insulation (suitable for electronic circuits)
Low moisture absorption (maintains stable performance in humid environments)
Flame retardant (UL94-V0 level, non-flammable)
Applications:
PCB (single-layer board, multi-layer board)
Electronic insulation material
Mechanical structural components
Because FR4 has both insulation, mechanical strength and heat resistance, it is widely used in PCB manufacturing and is one of the most common circuit board substrates.
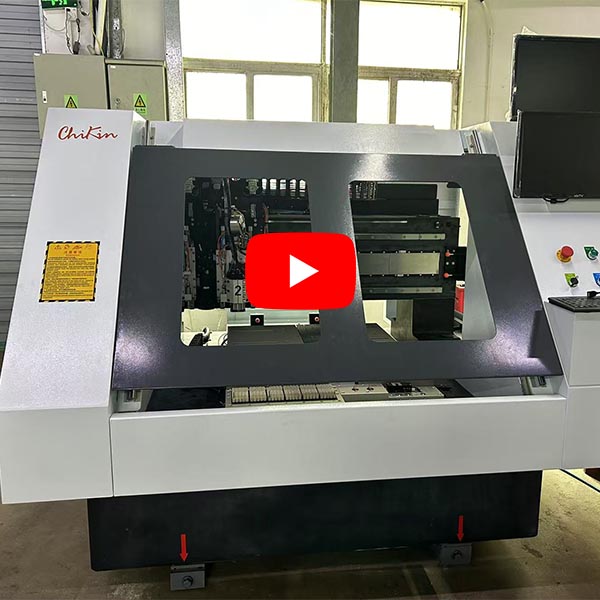
What do you need to know to make a PCB drilling machine?Making a PCB drilling machine involves knowledge and skills in multiple fields, including mechanical design, electrical control, software programming, and PCB processing technology. The following are the main contents that need to be mastered:
1. Mechanical structure design
(1) Machine tool design
Gantry or cantilever structure design
Guide and screw selection (high-precision ball screw, linear guide)
Spindle system (high-speed spindle, usually 50,000~300,000 RPM)
Automatic tool change system (ATC) to improve efficiency
(2) Precision motion control
High-precision servo motor or stepper motor to ensure drilling accuracy
Motion control algorithm (linear interpolation, circular interpolation)
Error compensation technology (temperature compensation, mechanical error compensation)
2. Electrical and control systems
(1) CNC system
Motion control card (such as DSP, FPGA or PC-Based control)
G code analysis (PCB drilling program is usually in Excellon format)
Visual alignment system (improve alignment accuracy)
(2) Electrical part
High frequency variable frequency drive (drives the spindle motor)
Power management (ensures stable power supply)
Safety protection circuit (overcurrent, overload protection)
3. PCB processing technology
PCB materials (FR4, CEM-3, high frequency materials, etc.)
Drilling process:
Micro holes (less than 0.1mm) and ordinary holes (0.2~0.5mm)
Multilayer board drilling (positioning accuracy requirements between different layers)
Laser drilling vs mechanical drilling
Vacuum cleaning system (clean drilling dust and prevent pollution)
4. Computer vision and automation
CCD visual alignment system (identify positioning points and improve drilling accuracy)
Automatic loading and unloading (robot or vacuum suction cup)
AI detection (drilling error analysis)
5. Software and data processing
CAM software support (Genesis, CAM350, AutoCAM)
G code analysis (Excellon or Gerber file processing)
Motion control software (LabVIEW, C++, Python)
6. Other key technologies
Environmental control (constant temperature and humidity, reducing material deformation)
Electrostatic protection (ESD) (avoiding electrostatic damage to PCB)
Production line automation (MES system, data traceability)
Summary
To make a PCB drilling machine, you need to comprehensively master mechanical design, CNC control, electrical automation, visual system, PCB process and other knowledge to create high-precision and high-efficiency equipment.
What part of your work are you currently doing? Are you doing whole machine design or focusing on a certain module?
What materials are PCB boards divided into?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) can be divided into the following main materials according to the substrate type. Each material is suitable for different electronic products and application scenarios:
1. Classification by substrate type
(1) Rigid PCB material
Used in most traditional electronic devices, with stable mechanical strength and electrical performance.
FR-4 (most common)
Composition: glass fiber cloth + epoxy resin + flame retardant
Features: high temperature resistance (TG value is usually 130°C~180°C), good insulation, flame retardant (UL94-V0)
Application: consumer electronics, automotive electronics, industrial control equipment, etc.
CEM-1, CEM-3 (economical alternative to FR-4)
Composition: glass fiber + paper base (CEM-1), or glass fiber + non-woven fabric (CEM-3)
Features: low cost, performance between FR-4 and paper substrate
Application: home appliances, low-end consumer electronics
High-frequency materials (PTFE, ceramic filling materials)
Composition: polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), ceramic filling materials
Features: low dielectric constant (Dk), low loss (Df), resistance to high-frequency signal interference
Application: 5G communication, satellite communication, RF microwave circuit
Metal-based PCB (aluminum-based, copper-based)
Composition: metal substrate (aluminum, copper) + insulation layer + Copper foil
Features: Excellent thermal conductivity, suitable for applications with high heat dissipation requirements
Applications: LED lighting, power modules, automotive electronics
(2) Flexible PCB materials (FPC)
Used for electronic products that need to be bent or folded.
PI (polyimide, Kapton)
Features: High flexibility, high temperature resistance (resistant to more than 300°C), chemical resistance
Applications: Smart phones, wearable devices, aerospace electronics
PET (polyethylene terephthalate)
Features: Low cost, general temperature resistance (usually less than 150°C)
Applications: Low-end FPC, such as keyboard membrane switches
(3) Rigid-flex PCB materials
Combining FR-4 and FPC materials to achieve a combination of rigidity and flexibility, suitable for complex structures.
Rigid part (FR-4) + flexible part (PI)
Features: foldable and maintains a certain mechanical strength
Applications: high-end consumer electronics, medical equipment, military electronics
2. Classification by heat resistance level (TG value)
**TG (glass transition temperature)** indicates the temperature at which the PCB material changes from hard to soft at high temperature.
TG value Material category Applicable scenarios
Ordinary TG (<130°C) Low-end CEM-1, CEM-3 General home appliances
Medium TG (130~170°C) FR-4 conventional materials Most electronic products
High TG (>170°C) Special FR-4, high-frequency materials Servers, automobiles, 5G equipment
3. Special PCB materials
Ceramic-based PCB (Al₂O₃, AlN)
Features: extremely high thermal conductivity, high temperature resistance
Application: military industry, power semiconductors, laser equipment
HDI PCB (high-density interconnect board)
Material: high TG FR-4, PI
Application: smart phones, chip packaging
Summary
The choice of PCB materials depends on the application scenario:
Ordinary consumer electronics → FR-4
High-frequency communication (5G, RF) → PTFE, ceramic filling materials
High-power heat dissipation (LED, power supply) → aluminum-based, copper-based
Flexible devices (mobile phones, wearables) → PI (polyimide)
High reliability (automobiles, servers) → High TG FR-4
Recent Posts

October 26, 2016
The Most Successful Engineering Contractor
May 12, 2025
China PCB Drilling Routing machine Development
May 06, 2025
PCB Design Process and Key Points






