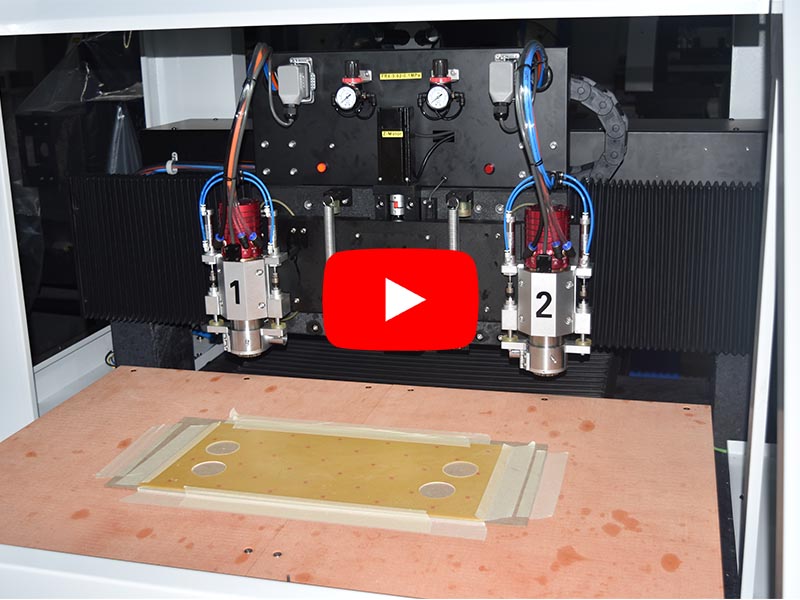
Which Method Process, SMT or Drilling?
Feb 13, 2025
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) designs use either through-hole (drilled holes) or SMT (Surface Mount Technology) based on the design requirements and application. Here's a breakdown of when to use each:
Through-Hole (Drilled Holes)
Through-hole technology involves drilling holes in the PCB to mount components with leads that pass through the board. This method provides strong mechanical connections and is commonly used in specific high-power or high-frequency applications.
When to Use Through-Hole:
- High-power applications: Components that handle higher power or require stronger connections, such as power supplies or RF circuits, often use through-hole.
- Longer leads/components: Components like resistors, capacitors, and transformers with longer leads might require through-holes for secure mounting.
- Mechanical strength: Through-holes provide stronger connections for components that might experience stress, such as in automotive or industrial equipment.
- Via connections: For multi-layer PCBs, through-holes (vias) are used to connect the different layers of the PCB.
SMT (Surface Mount Technology)
SMT involves mounting components directly on the surface of the PCB, with no leads passing through the board. SMT components are smaller and more suitable for automated production processes, making it ideal for mass production.
When to Use SMT:
- Miniaturization: SMT is great for space-saving designs, which is why it's used in mobile phones, laptops, and compact devices.
- High-volume production: Since SMT components are smaller and easier to automate, it's ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
- Low-power or signal circuits: SMT is commonly used for low-power or low-frequency circuits, such as in consumer electronics or signal processing applications.
- Multilayer PCBs: In multi-layer designs, SMT is typically used for surface-mounted components, while through-holes handle connections between layers.
Hybrid Approach
Many modern designs use a combination of both techniques, especially when dealing with complex PCBs. SMT is used for the majority of components, while through-holes are added where needed for things like power connections or vias between layers.
In short:
- Through-Hole: Best for high power, mechanical strength, or multi-layer connections.
- SMT: Best for small, high-volume, low-power designs where space is a concern.
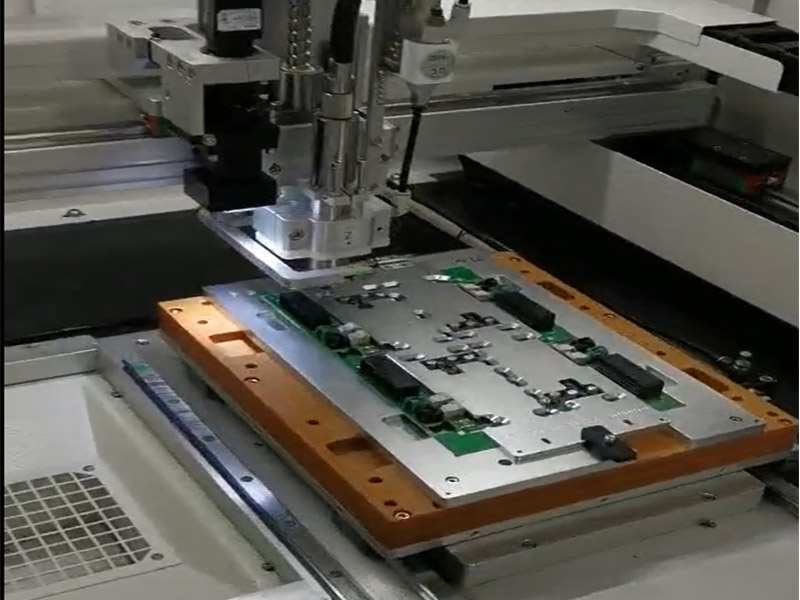 The choice between the two largely depends on the design's electrical and mechanical requirements, as well as production volume.
The choice between the two largely depends on the design's electrical and mechanical requirements, as well as production volume.
Recent Posts

October 26, 2016
The Most Successful Engineering Contractor
May 12, 2025
China PCB Drilling Routing machine Development
May 06, 2025
PCB Design Process and Key Points






